- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Architecture and infrastructure
Network between companies and nodes
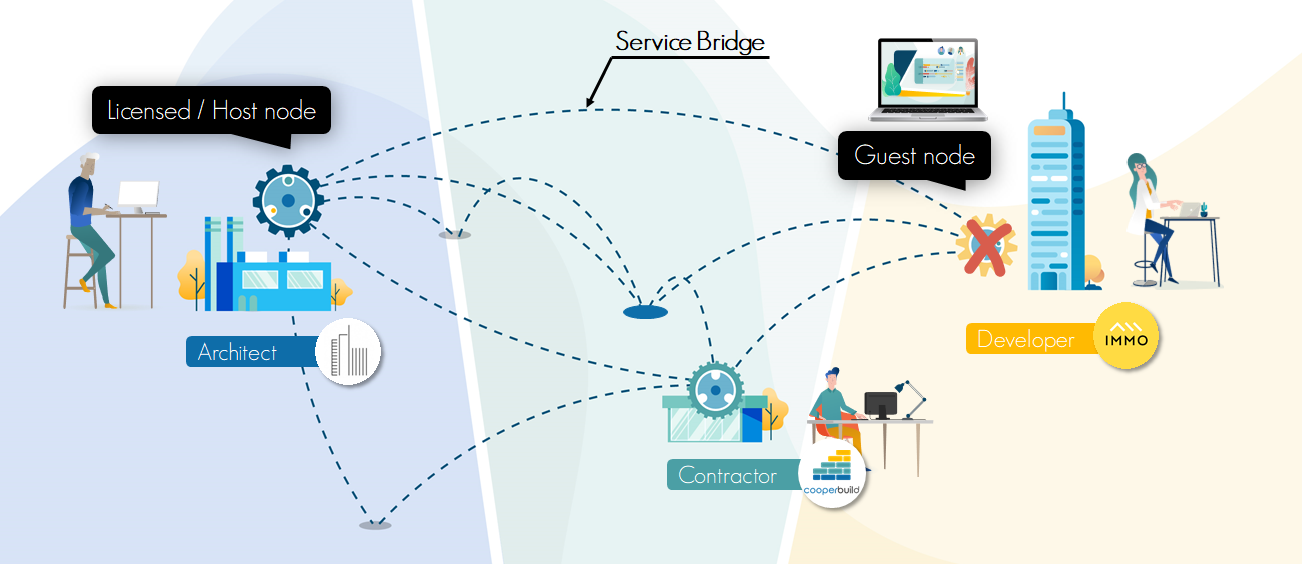
Each organization identified in the Cooperlink network is assigned a tenant and a dedicated database -referred to here as Node - which ensures the autonomy of each organization. As illustrated in the articles above, Cooperlink is based on a proprietary message broker / ESB* technology - referred to here as Service Bridge. The latter is intended to link the nodes together and ensure the synchronization of information according to the defined access rights.
The Service Bridge supports the transport of all types of data available on Cooperlink, including documents that are cut into fragments (chunking). The exchange of information takes place through a workspace that defines the organizations and their access rights.
Cooperlink distinguishes 2 types of nodes:
- Host (licensed): the licensee has his own node and chooses the infrastructure on which he wants to install it. He can also integrate his own tools.
- Guest : a guest partner on Cooperlink has his own node but the data is hosted by the host. He cannot integrate his own tools. The segregation of data is nevertheless ensured.
(*) Enterprise Service Bus
This networked structure allows each organization to be fully autonomous. This is because each organization with a licensed node fully manages its own environment and integrations independently, without providing any access to its partners.
The workspace is the meeting point between these organizations. The Bridge Service is responsible for ensuring the dissemination of the right information. Workspace settings are used to define rules for distributing information (such as automatic or manual modes).
Host infrastructure
Each Cooperlink host can choose the type of hosting of its node:
| Cooperlink Cloud | On-premise | |||
| Node location | Full cloud | Shared Cloud | Dedicated Cloud | Customer Infrastructure |
| Infrastructure Management | By Cooperlink | By Cooperlink | By Cooperlink | By the customer |
| Service Management | By Cooperlink | By Cooperlink | By Cooperlink | By Cooperlink |
| Storage Management | Cloud storage managed by Cooperlink. No integration with enterprise tools | Storage on enterprise tools (cloud only) | Storage on enterprise tools (cloud only) | Storage on enterprise tools (cloud and/or on-premise) |
| Database | Dedicated on shared infrastructure | Dedicated on shared infrastructure | Dedicated on dedicated infrastructure | Dedicated on customer infrastructure |
| Node migration | Currently not available | Currently not available | Available | Available |
Shadow storage
For security reasons, Cooperlink uses shadow storage, i.e. buffer storage that includes versions of documents shared in workspaces on Cooperlink. This creates a protective barrier: partners do not access documents from the source (e.g. sharepoint), and Cooperlink workspaces are protected from unintentional manipulation by internal users. Shadow storage also allows recovery of deleted documents.
Guest partners access documents through this shadow storage. Partners with their own node access documents from their own environment.
Data localization
Cooperlink Cloud data is located in Europe (Belgium) with the service provider Combell. The data is replicated in 2 physically separated data centers offering a Disaster Recovery mechanism and an availability rate of 99.99%.

The data in case of on-premise installation are entirely located in the Customer's infrastructure.
Shadow storage is located either in the cloud or in the customer's infrastructure.


