- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Settings of a Workspace for Document Management
This article applies to BOOST EMPOWER GUEST (free) licenses
Purpose and scope
This article details each setting for configuring workspace documents.
Prerequisite
Changing the configuration of documents in a workspace requires the appropriate rights (see Roles and permissions for the members of a workspace)
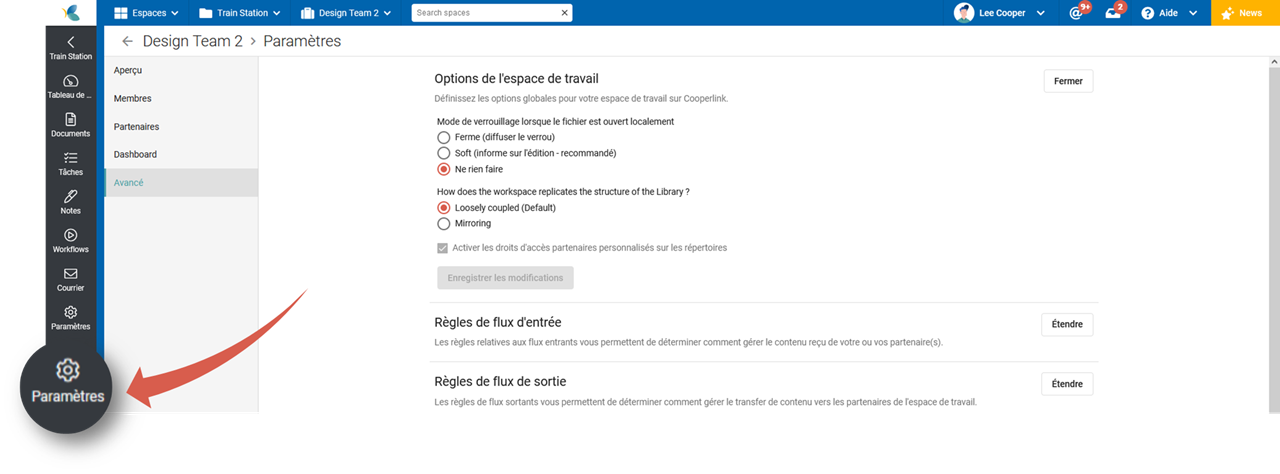
Access to document configuration
In the workspace, use the left menu and click Settings. Then select the Advanced tab. The sections covered by this article are:
- Workspace Options
- Input flow rules
- Output flow rules
- Configuring document management
Workspace Options
The first tab defines three particularly important workspace settings.

Lock mode
This option allows you to set the behavior of the workspace when it detects a file being edited on the server or through Cooperlink.
Using custom partner access rights on directories
Access rights are used to assign permissions to workspace partners. They help protect the workspace from unwanted publications and changes. For more information, see Terminology and matrix of access rights.
How it works
You can choose between two operating modes that determine the management algorithm between the data sources and the workspace. This mode has an important influence on the document structure of the workspace and the links created.
| LOOSELY COUPLED | MIRRORING | |
| Use Cases | Limited document sharing. Simple projects / Datarooms. | Large document shares. Complex multi-partner projects. |
| Benefits | The end user completely freely defines the document structure of his workspace and the name displayed in the workspace. | The document structure is subject to certain constraints to ensure mirror replication, with the exception of user-defined links (anchor points). |
| Disadvantages | Tracking name changes and file or directory movements is not active. | Tracking name changes and file or directory movements is active. |
| Illustration | 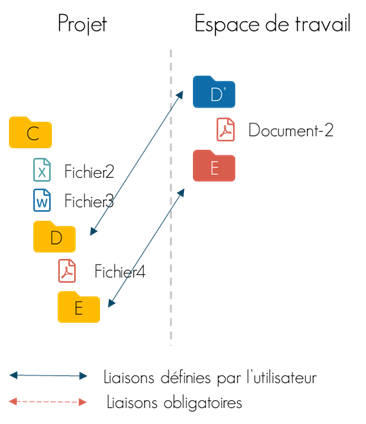 | 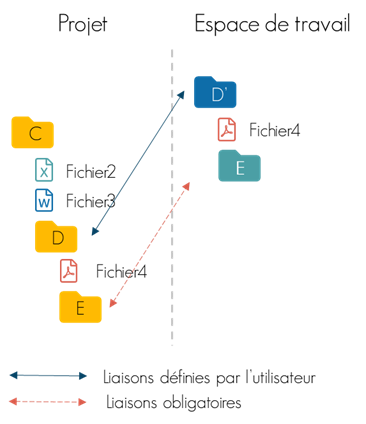 |
Management of incoming and outgoing flows
Cooperlink is a transactional platform, i.e. it manages incoming information exchanges and incoming flows. It is possible to configure these two flows independently. The following table shows the recommended configurations :
Menstruation | Fully automatic in both directions | Output Manual Automatic input |
| Output stream |   |   |
| Input flow |   |   |
Configuring document management
Go to the Document Management Configuration section of the Advanced tab.
Document cards
Select the map templates that you want to use when uploading a document, and when viewing in the workspace.
For more information about maps, see What is a card?.
Code and documentary uniqueness
This area allows you to configure the document code and the uniqueness criterion.
To create a document code or uniqueness criterion, define an appropriate mask based on the document information (see Fields identifiers in cards and dynamic masks).
Example mask: GARE-{{std_building_type}}-{{std_building_activity}}{{std_building_no_fiche:##000}}
Result: GARE-FTE-001-AR
Extracting metadata
Extracting metadata from the file name uses RegEx notation (regular expression) as follows:
- Groups enclosed by parentheses refer to metadata keys. The identification of the key concerned is carried out using the syntax (?<key>...).
- An additional check is performed by Cooperlink to validate that the extracted value conforms to the metadata definition (e.g. that the value is part of the list of predefined values).
Example of a regular expression: GARE-(?<std_building_type>[a-zA-Z]{1,4})-(?<std_building_no_fiche>\d{1,3})-(?<std_building_activity>\w{1,3})
Custom file names at download
This section allows you to customize the names of files when downloading.
To create a custom name, define an appropriate mask based on the document information (see Fields identifiers in cards and dynamic masks).
Example mask: {{document_code}}-{{name}}-{{version}}
Result: GARE-FTE-001-AR-FileName-202108201745Z.pdf


